Finding Purpose and Meaning In Life (note from coursera)
Link to the course: https://www.coursera.org/learn/finding-purpose-and-meaning-in-life
If your life has a purpose, – you will increase likelihood that
Resilience – the ability get recovery from the bad day
Improve DNA repair
Antibody production
Having longevity
Sleep improvement
Diet improvement
HbA1C management better
More money
And decrease the likelihood of
Cognitive conflict because you have a clear direction to go
Fear response – you can bounce back from the fear
Inflammation
Depression
Stroke
Heart attack
Alzheimer disease
Job burnout
Public health – existentialist
Human being;
Work – balance and meaningful work
School – how do you decide your life, what is your future career
Family – purposeful unit for individuals and communities
Aging – repurposing after the retirement; people who have a health problem –
Making the analogy
Tree
Root – purpose
Other parts are the things that you have to adapt toward the root
He introduces the app “purposeful”
Three things will be involved – all are overlapped;
Science
Philosophy – this creates science at the beginning
Practice – how to apply it
What is the purpose in life?
Central, self-organizing life aim
Motivate all resources toward that particular goals
Theme – it relates to yourself
What are your values? asking these questions: and write the answers for each question
What matter most
Who relies on you
Who inspires you
What causes do you care about
What are you grateful for
What gets you out of bed in the morning
How do you want to be remembered
Talking about life – what if human have forever life, how would you live your life
What if you know, you are going to die tmr, how would you live your life
Making an analogy with, what if you have only 5 dollars in your pocket, and random
Thinking about death – create more life
Headstone test [ชื่อบนป้ายหินหลุมศพ]
What would you want on you headstone
What would you want the people say about you or the mark that you left for this world
- Your legacy, mission to others
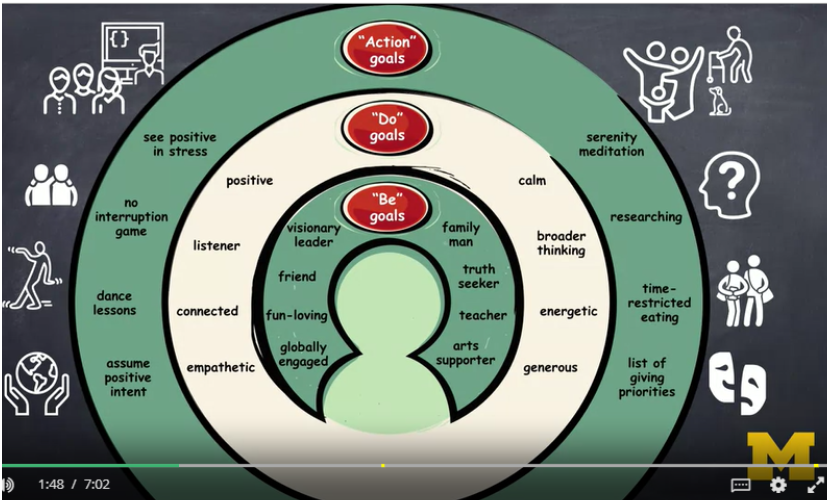
Be goals
- Purpose in life
Purpose can be changed over time
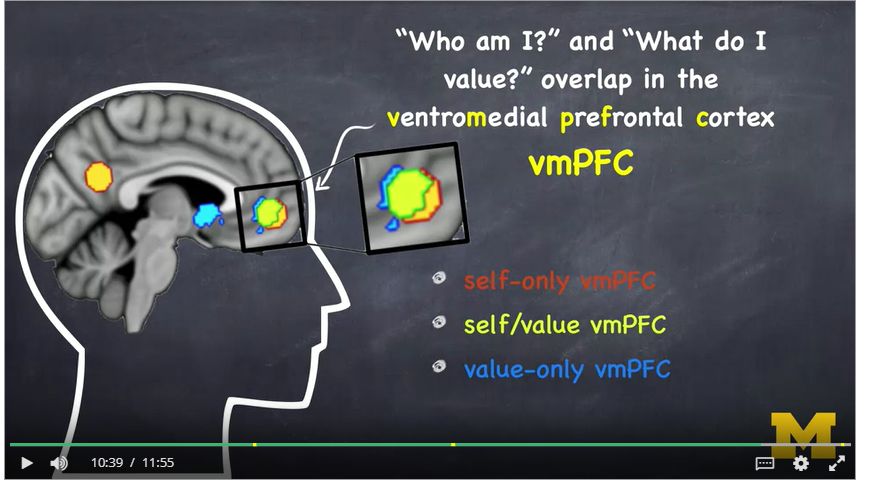
If links to 2500 year old of MRI – atman (little dot on Bhuddha's forehead)
Two forms of happiness (Aristotle)
- Eudaimonic (care about others) – well-being – less depressive symptom
- Hedonisic (self-centric) – ill-being – more depressive symptom
- Ventral striatum – reward system ที่จะดูว่าความสุขที่เกิดขึ้นมา มาจากความรู้สึกที่ได้รับ หรือมาจากการให้โดยการถามคำถาม ซึ่งคนที่มีความสุขแบบ eudaimonic จะเป็นความสุขที่เกิดจากการให้ แต่ hedonisic เป็นความสุขที่เกิดจากการได้รับ สิ่งที่ study ข้างล่างได้ทำคือ ถามคำถามว่าถ้าให้เงินไปแล้ว จะทำอะไรกับมันบ้าง 1.ให้เงินกับตัวเองไม่แบ่งใคร 2.ให้กับตัวเองบ้างและแบ่งให้คนอื่นบ้าง – แล้วดู relation ที่เกิดขึ้นจากการ activate ของสมองในส่วนดังกล่าว
Related study that he mentioned: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.1323014111
ในวีดีโอก็พูดถึง amygdala ซึ่งเป็นส่วนของสมองที่ตอบสนองเกี่ยวกับความกลัว – มีงานวิจัยที่โชว์ว่าคนประเภท Eudaimonic เมื่อเจอคำข่มขู่ สมองส่วนนี้จะโดน activate น้อยกว่ากลุ่มคนที่อยู่ในพวก Hedonisic ว่าแล้วนึกถึง post เก่าของตัวนี้ https://t-lerksuthirat.blogspot.com/2018/11/which-one-do-we-feed.html
Example for purposeful people – to make it easier to understand
Suggested reading materials that I found they were very interesting:
What Kind of Cook Are You?
S. Kierkegaard, The Journals of Kierkegaard 1834–1854, trans. and ed. Alexander Dru (Fontana: 1958), 44, from Gilleleie, August 1, 1835.
A.R. Albertsen, “The Relation Between Faith and Ethics in Kierkegaard’s Fear and Trembling,” Teología y Cultura 15, no. 10 (2013).
C. Pretus, N. Hamid, H. Sheikh, et al. “Ventromedial and Dorsolateral Prefrontal Interactions Underlie Will to Fight and Die for a Cause.” Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience (2019): 569-577.
B. L. Arnold and L. S. Lloyd, “Harnessing Complex Emergent Metaphors for Effective Communication in Palliative Care: A Multimodal Perceptual Analysis of Hospice Patients’ Reports of Transcendence Experiences,” American Journal of Hospice & Palliative Medicine no. 31 (2014): 292–99.
Purposeful: Be, Do, and Action Goals
E. T. Berkman, J.L. Livingston, L.E. Kahn. “Finding the ‘Self’ in Self-Regulation: The Identity-Value Model,” Psychological Inquiry 28 (2017): 77-98.
B.W. Smith and A.J. Zautra. “The Role of Purpose in Life in Recovery from Knee Surgery. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine 11 (2004):197-202.
- งานนี้น่าสนใจดี ตรงที่ว่า การมี purpose in life มันไป buffering stressor (ความกดดันต่าง ๆ เช่น การไม่ได้ในสิ่งที่ต้องการ ความยากจน การดูถูกเหยียดหยาม การสูญเสียคนรัก การสูญเสียงาน เป็นต้น) ทำให้ resilience ค่อนข้างดี
- งานนี้น่าสนใจดี ตรงที่ว่า การมี purpose in life มันไป buffering stressor (ความกดดันต่าง ๆ เช่น การไม่ได้ในสิ่งที่ต้องการ ความยากจน การดูถูกเหยียดหยาม การสูญเสียคนรัก การสูญเสียงาน เป็นต้น) ทำให้ resilience ค่อนข้างดี
Suggested reading:
T. L. Jacobs, E. S. Epel, J. Lin, E. H. Blackburn, et al. “Intensive Meditation Training, Immune Cell Telomerase Activity, and Psychological Mediators,” Psychoneuroendocrinology 36 (2011): 664–81.
(เรื่อง Psychoneuroendocrinology เคยเรียนสมัยตอน take basic course ป.เอก สอนโดย อ.ภาควิชาพยาธินี่แหล่ะ)
Study นี้ก็ดูน่าสนใจดี คือลองทำ survey ว่าในแต่ละปี นศ.ใหม่ที่เข้ามา focus กับเรื่องอะไร
แล้วลองมาดู study ที่ดูความสัมพันธ์ระหว่าง ความสามารถในการหาเงิน vs ความสุข
การมี purpose – มันจะ buffering stress ที่เกิดจาก finance ได้










Comments
Post a Comment