Note: Protecting the aging genome
มาดู theme ของการเข้าสู่สังคมผู้สูงวัย
Note: Protecting the aging genome
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2019.12.001
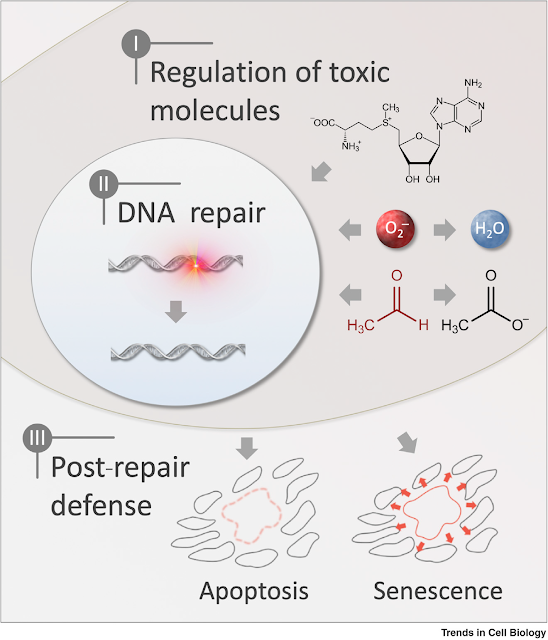
Three main layers protect the accumulation of DNA damage
Reducing damaging molecules (antioxidant)
Repairing DNA damage
Inducing senescence/apoptosis to response to persistent DNA damage
The end of this paper -- help to propose novel interventions which increase healthspan!!
DNA repair is quite conserved and important for living organisms as stated above.
Markers of DNA damage - observe in age-associated disease
Obvious evident -- ppl who has defective in DNA repair -- show features of premature or accelerated aging
Defect in different pw --aging features in different tissues;
Cockayne syndrome, ataxia-telangiectasia -- premature neurological aging
Werner syndrome, Hutchinson-Gilford progeria -- cardiovascular aging
>50 DNA repair disorders described with various degrees of overlapping phenotypes with aging -- > suggest different types of DNA damage -- > different pathologies in aging
Most common oxidative DNA lesion -- mutagenic 8-oxoguanine -- > accumulate in several tissues with age
ss and db strand DNA break -- activates PARP1 -- activity of this enzyme increase with age -- >strand break accumulate in elderly
DSB markers; 53BP1 and gH2AX -- increased with age across multiple tissues and in senescent cells
Consequences if DNA is left unrepaired
Three outcomes; but altered with age
Cell transform and become cancerous
Entering non proliferating state (senescence)
Die through apoptosis
Cell death
Apoptosis
With age, apoptotic activity changes
Heart, kidney, skeletal muscle, and T cell
Increased apoptosis -- contributing to loss of cellularity (causing increased production of free radicals) but it helps to prevent the accumulation of mutation in DNA
Colon
Apoptosis -- decrease with age
Parthanatos
DNA damage is central to its initiation
Activation of DNA damage responder PARP1 -- formation PAR polymers -- activation of apoptosis -inducing factor + caspase-independent cell death
Cell senescence
If a cell invades death on DNA damage -- > usually cells enter senescences. Several ways to induce senescence;
Replicative senescence in somatic cells
Oncogene-induced senescence
Excessive DNA damage
Younger age -- senescence helps
Tumor suppression
Wound healing
Tissue development
Drugs that clear the senescence cells ~ senescences have been believed to cause chronic diseases (senescence cells ~ so many accumulated mutations)
Senolytic drug postpone age-associated pathologies in humans
Future perspectives ~ development interventions through DNA repair
Few molecules - may directly stimulate DNA repair
RAD51-stimulatory compound 1 (RS-1) -- increase HR
Nicorandil -- stimulate base excision repair through APE1 enzyme
Aspirin - -- stimulate NER
Modulation of DNA damage response -- impact aging
Inhibition of PARP1 -- lifespan extension in certain model organisms
Age-associated activation of PARP1 -- relate to persistent DNA damage foci -- 53BP1, gH2AX, FOXO4 in aging cells
Keys
NAD+:NADH ratio
Energy sensor (AMP-AMPK)
Outstanding questions --
A large gap between biochemistry and clinical phenotypes
Much information in mechanistic but could not well-explain clinical outcomes
(I think a major problem is the ecosystem to support communication between clinicians and researchers).
Do small-molecules DNA repair stimulators attenuate aging?
Does decreasing DNA repair efficacy explain variability in aging phenotypes?
DNA repair declined with age
No clear connection between tissue specific vs DNA repair efficacy decline
No clear connection between age-associated phenotypes vs DNA repair efficacy decline
How the heck can we measure DNA repair stimulators at a clinical level? -- > functional markers, I think
















Comments
Post a Comment